Diseases Caused by Physical Inactivity
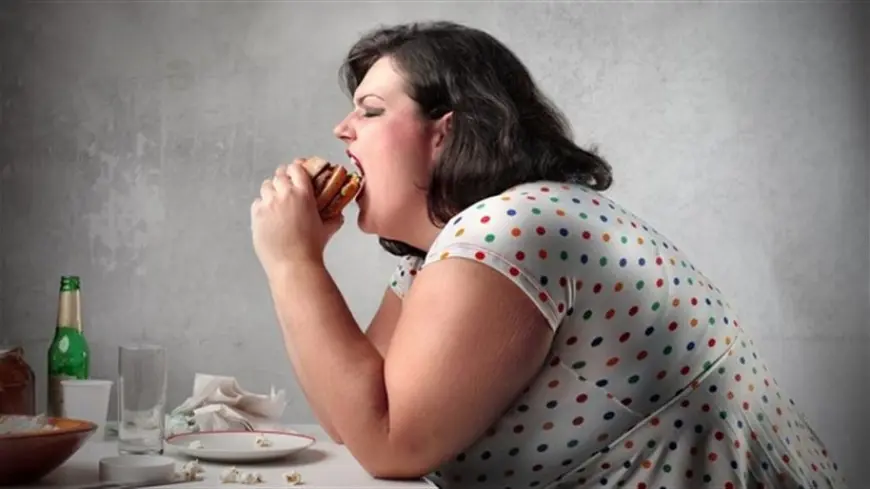

Being physically active strengthens both physical and mental health, increases the ability to perform physical and intellectual tasks, and boosts the immune system. On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to the development of various diseases. One such condition is obesity.
Obesity is the excessive accumulation of fat in subcutaneous tissues and body organs. It does not only result from lack of movement but can also arise due to several other factors:
Genetic Predisposition
Individuals with close relatives who are overweight are at a higher risk of becoming obese.
Caloric Intake Exceeding Caloric Expenditure
Consuming high-calorie foods rich in animal fats and fast-digesting carbohydrates is one of the most widespread causes of obesity. When people eat poorly and move little, the body’s energy balance is disrupted. In other words, the amount of calories consumed exceeds the amount burned during physical activity. The excess calories are stored as fat in the body.
Emotional Stress
Some people tend to eat when they are anxious, angry, or sad. Favorite comfort foods — especially sweets — may improve mood temporarily. However, if this behavior becomes habitual, body weight gradually increases.
Overeating Habits
Tasting food constantly or eating leftovers even after feeling full — habits commonly observed in women — can lead to fat accumulation in the body over time.
Health Conditions
Slowed metabolism and endocrine (hormonal) disorders can also lead to weight gain.
Why Is Obesity Harmful?
Obesity not only alters a person’s appearance but also seriously harms their health. Diseases that may result from obesity include:
-
Diabetes (type 2)
-
Musculoskeletal disorders
-
Cardiovascular diseases
-
Digestive system diseases
-
Infertility
Healthy Habits to Prevent Obesity:
-
Eat small meals 5–6 times a day.
-
Consume low-calorie foods rich in proteins, slow-digesting carbohydrates, vitamins, macro- and micro-elements.
-
Choose lean cuts of meat, fish, and dairy. Replace animal fats with plant-based oils.
-
Healthy fatty acids like Omega-3, Omega-6, and Omega-9 are found in fish, seafood, olives, ghee, and nuts.
-
Fruits, vegetables, and greens positively affect metabolism and help speed up fat burning.
-
Drink green tea daily. Its flavonoids aid digestion and protect the body from harmful free radicals.
-
Follow a light, plant-based diet one day per week — eating soups without meat or fat, porridge (from wheat, lentils, buckwheat, rice).
-
Have dinner at least 3 hours before bedtime.
-
Drink a glass of water 30 minutes before meals.
-
When under stress, avoid calming yourself with food. Instead, listen to music, read a book, or watch television.
-
Limit consumption of salty, pickled, canned, fast food, and sweets.
-
Weigh yourself once a week.
-
Those at higher risk of obesity (due to family history, diabetes, or slow metabolism) should consult their doctor regularly.