Why does it get dark before our eyes?
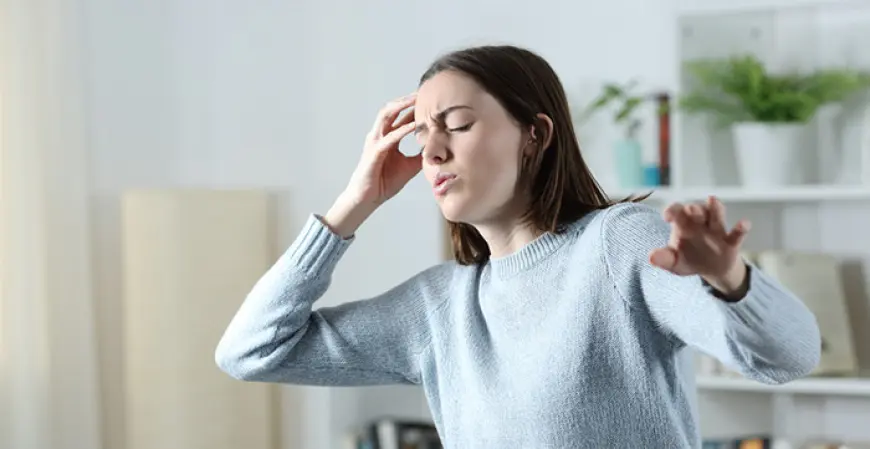

This usually happens due to a rapid drop in blood pressure to the brain. As a result, the brain doesn’t receive enough nutrients and oxygen, and it cannot properly process the information coming from the eyes, which causes various visual effects.
In many cases, the body quickly restores circulation, and the darkening of the eyes lasts only a few seconds. For example, this can happen when you stand up quickly after sitting for a long time. However, sometimes it signals a more serious problem.
Darkening of the eyes can lead to fainting, which in turn can result in severe falls or a concussion. If the brain stays without oxygen for a long time, its tissues begin to die, which presents a serious threat to life.
Therefore:
If someone loses consciousness and doesn't regain it within 1 minute — emergency medical help should be called.
If the darkening of the eyes lasts for several minutes — it is also important to urgently seek medical assistance.
There are many causes of darkening of the eyes. Here are the most common ones:
Orthostatic hypotension: A sharp drop in blood pressure when standing up. Blood rushes to the legs and abdomen, and the brain doesn’t get enough blood. Possible causes:
-
Dehydration (due to diarrhea, high temperature, heavy sweating).
-
Heat or overheating (sunstroke).
-
A drop in blood sugar levels.
-
Digestive problems (some people experience a drop in pressure after eating).
-
Anemia (low blood count).
-
Being at high altitudes.
-
Pregnancy.
-
Excessive alcohol consumption.
-
Some medications (diuretics, antidepressants, antihypertensive drugs, etc.).
-
Some diseases (diabetes, thyroid disorders, nervous system disorders).
-
Poisoning (e.g., carbon monoxide or other chemicals).
Vasomotor fainting (neurocardiogenic syncope): This occurs due to an excessive response of the nervous system to certain triggers. The heart rate slows down, and blood pressure drops. Possible triggers include:
-
Strong emotional stress.
-
Prolonged stress.
-
Fear (for example, before an exam or a dentist appointment).
-
The sight of blood.
-
Intense physical exertion (e.g., during defecation).
If the darkening of the eyes happens only once and passes quickly (e.g., after standing up quickly or overheating) — there is no need to worry too much. The best thing to do in this situation is to lie down and elevate your legs slightly. This will help direct blood to the brain and improve your condition. Afterward, stand up slowly and carefully.
If darkening of the eyes occurs frequently (several times a day or week), you should consult a therapist.
The doctor will examine you and, if necessary, order blood tests and a heart examination. After the examination, the doctor will give recommendations:
-
Drink enough water (2.7 liters per day for women, 3.7 liters for men).
-
Eat small meals more frequently.
-
Engage in regular physical activity.
-
Avoid alcohol consumption.
-
Take vitamins and supplements (especially iron and vitamin B12) only as prescribed by a doctor.
-
Moderately increase salt intake (if recommended by a doctor).
-
Sleep with your head elevated.
If necessary, the therapist will refer you to specialists — a neurologist, endocrinologist, or cardiologist.